Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
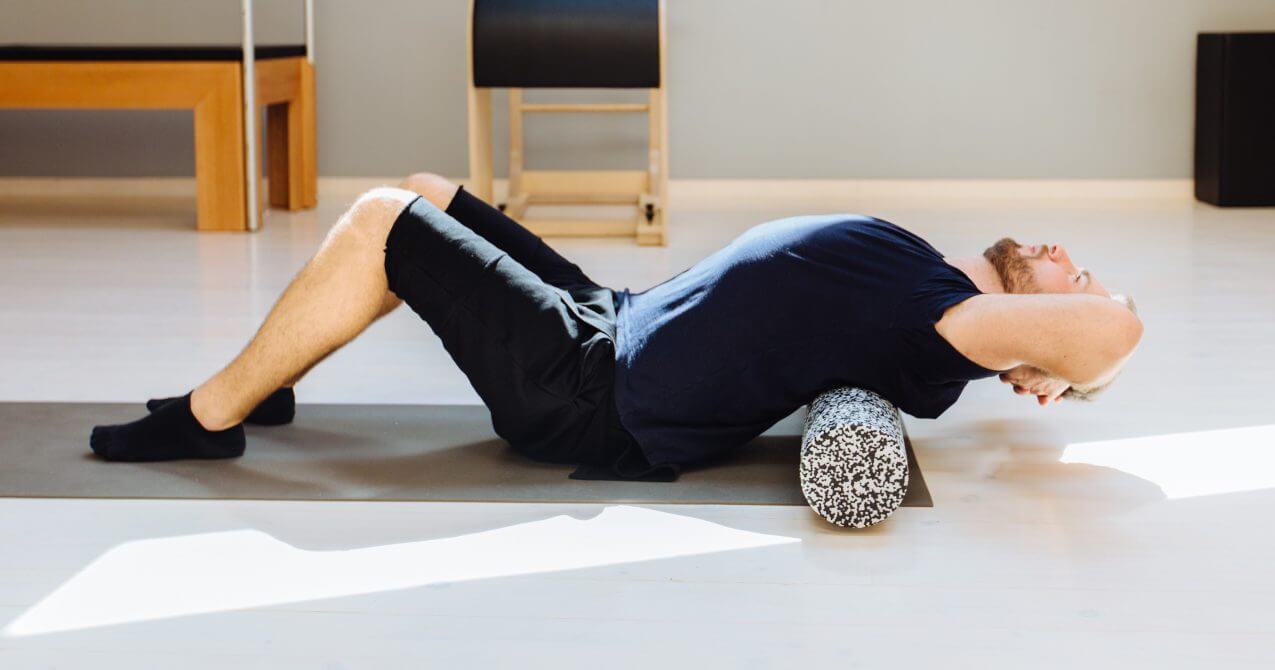

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
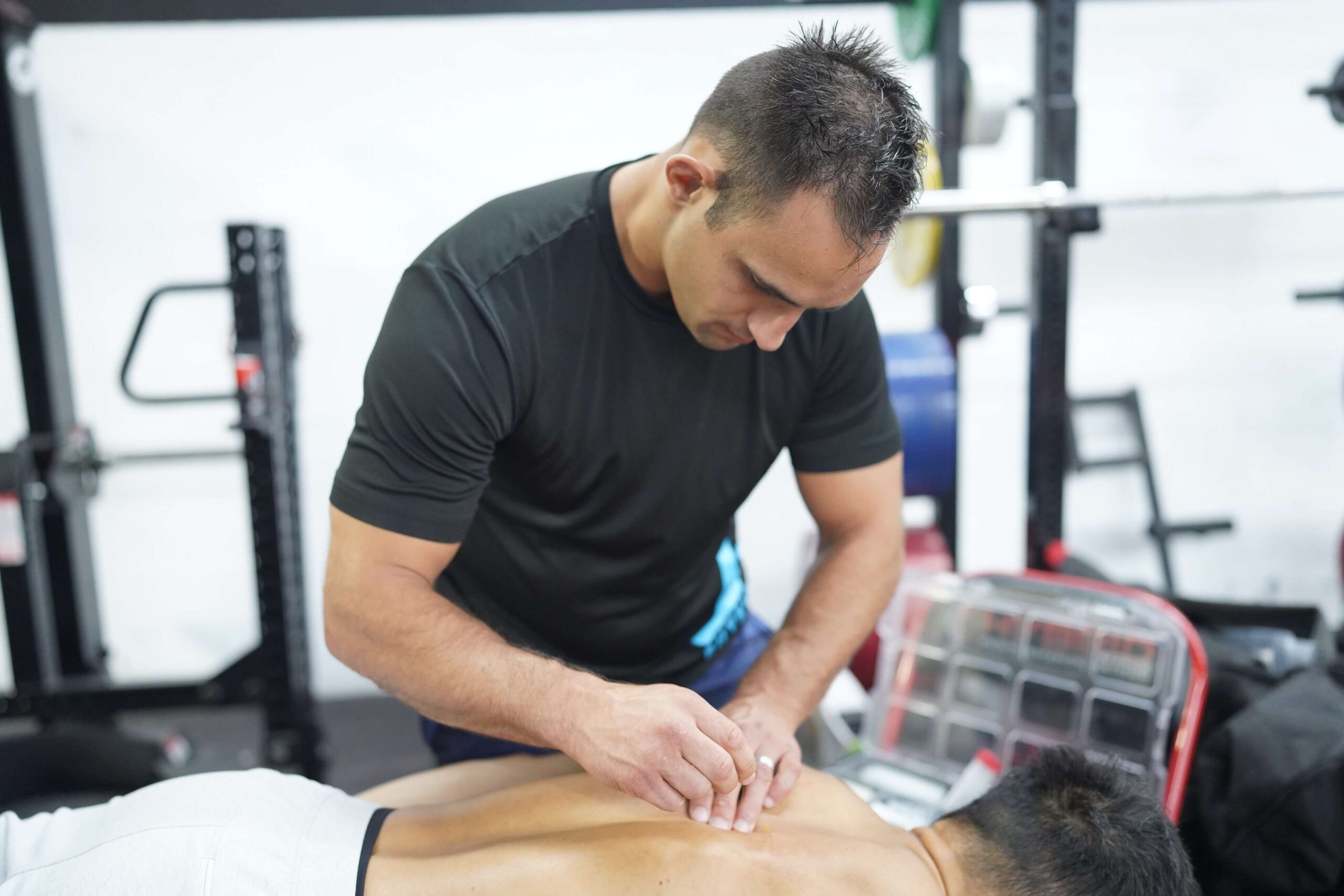

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
4. Insufficient Recovery: Lack of adequate recovery time between workouts can contribute to the buildup of muscle tension.
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
3. Injuries: Bruises, strains, and other injuries can cause muscle spasms and tightness. This is particularly relevant for contact sports like wrestling or football.
4. Insufficient Recovery: Lack of adequate recovery time between workouts can contribute to the buildup of muscle tension.
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
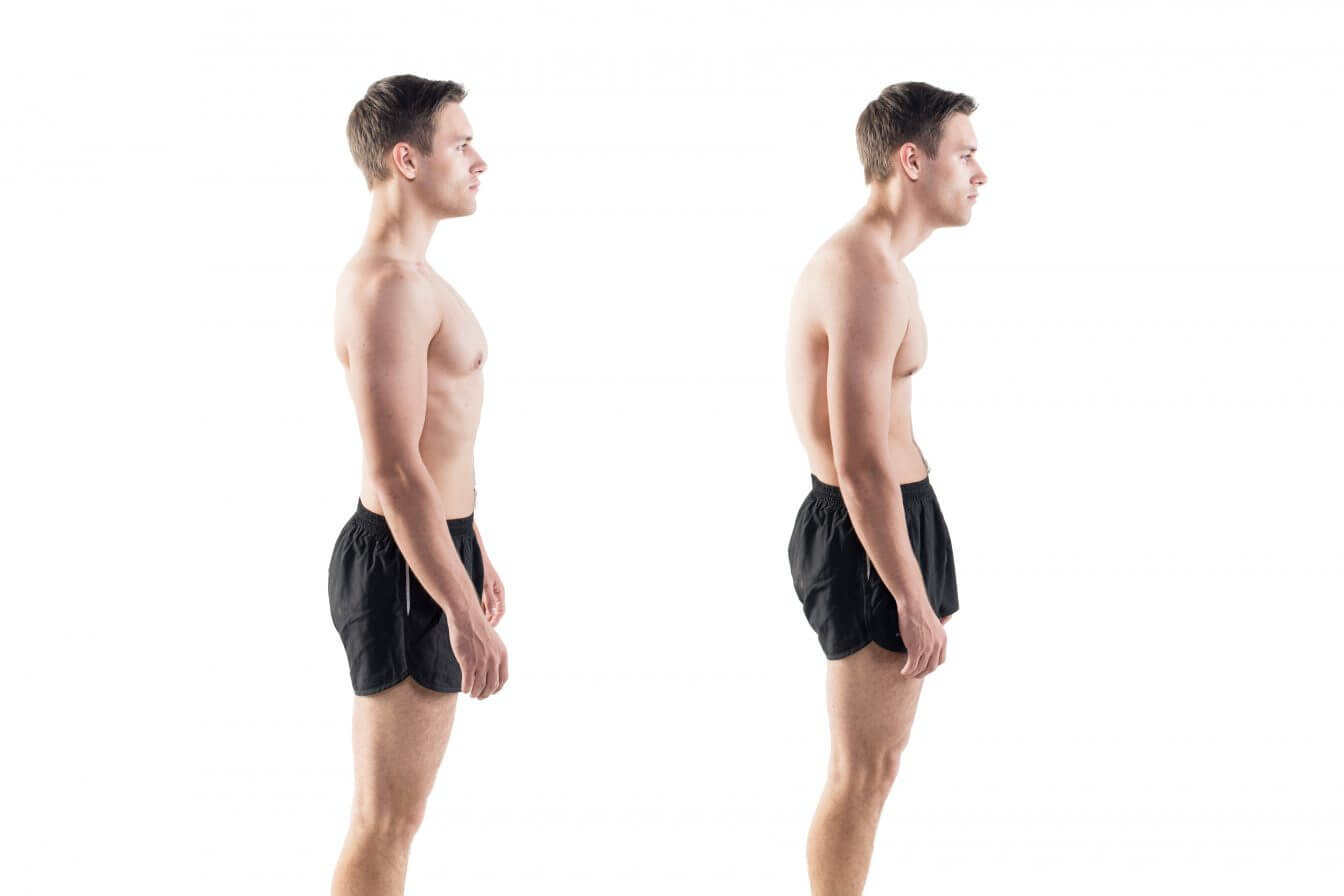
2. Poor Posture: Maintaining an improper posture for extended periods, especially during exercises or in daily life, can lead to muscle tightness under the shoulder blade.

3. Injuries: Bruises, strains, and other injuries can cause muscle spasms and tightness. This is particularly relevant for contact sports like wrestling or football.
4. Insufficient Recovery: Lack of adequate recovery time between workouts can contribute to the buildup of muscle tension.
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com
1. Muscle Overuse: Continuous intense training can lead to muscle overuse and spasms. This is often seen in swimmers, tennis players, and throwers, whose muscles are constantly subjected to high loads.
2. Poor Posture: Maintaining an improper posture for extended periods, especially during exercises or in daily life, can lead to muscle tightness under the shoulder blade.

3. Injuries: Bruises, strains, and other injuries can cause muscle spasms and tightness. This is particularly relevant for contact sports like wrestling or football.
4. Insufficient Recovery: Lack of adequate recovery time between workouts can contribute to the buildup of muscle tension.
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com

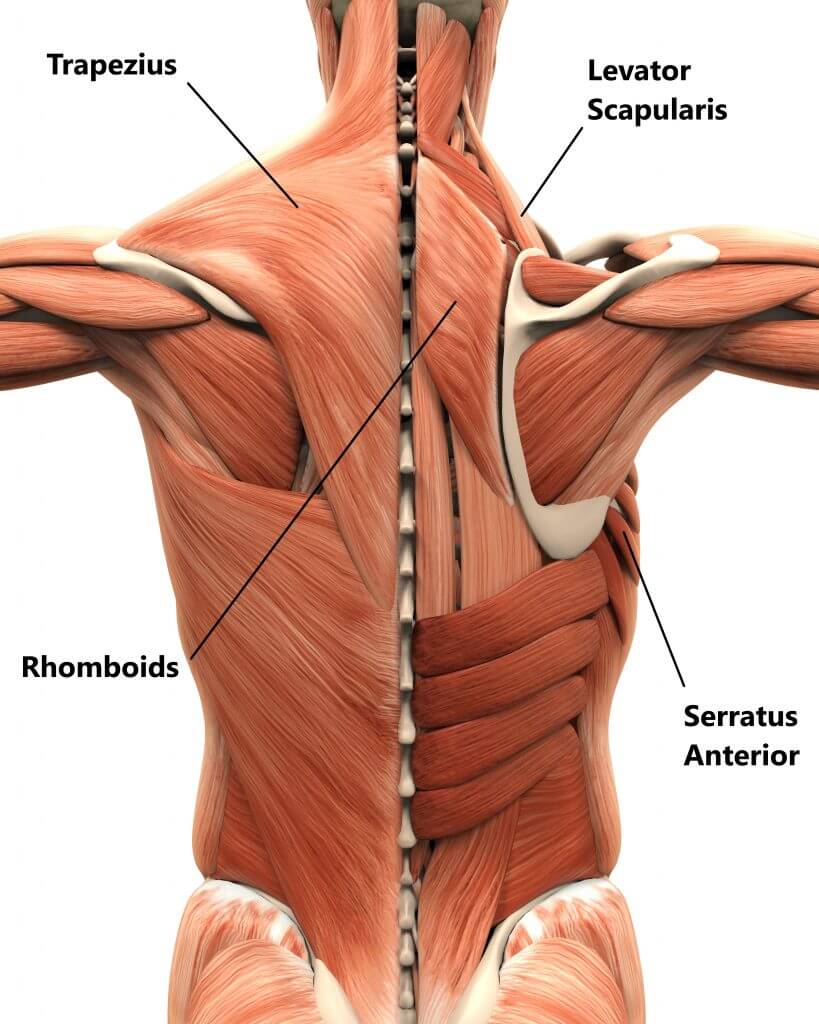
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a common issue among athletes, especially those involved in sports that place a high demand on the upper body. This condition can cause significant discomfort and restrict movement, negatively affecting athletic performance.
1. Muscle Overuse: Continuous intense training can lead to muscle overuse and spasms. This is often seen in swimmers, tennis players, and throwers, whose muscles are constantly subjected to high loads.
2. Poor Posture: Maintaining an improper posture for extended periods, especially during exercises or in daily life, can lead to muscle tightness under the shoulder blade.

3. Injuries: Bruises, strains, and other injuries can cause muscle spasms and tightness. This is particularly relevant for contact sports like wrestling or football.
4. Insufficient Recovery: Lack of adequate recovery time between workouts can contribute to the buildup of muscle tension.
1. Pain Under the Shoulder Blade: Sharp or dull pain that worsens with movement of the arm or shoulder blade.
2. Limited Mobility: Difficulty in lifting the arm or performing certain movements.
3. Spasms and Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and spasms in the shoulder blade area.
1. Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy sessions can help relieve tension and improve mobility. Key methods include massage, stretching exercises, and manual therapy.

2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders can help prevent recurrence. Examples include pectoral stretches, the “cat-cow” exercise, and exercises with resistance bands.

3. Proper Posture: Maintaining proper posture both during workouts and in daily life is crucial. Using ergonomic chairs and taking regular breaks to stretch can help prevent muscle tightness.
4. Ice and Heat: For acute pain, ice can be used to reduce inflammation, followed by heat to relax the muscles.
5. Medication: In some cases, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by a doctor can be helpful.
Muscle tightness under the shoulder blade is a problem many athletes face. However, with timely and proper treatment and prevention, the risk of this issue can be significantly reduced, and the quality of training and athletic performance can be improved. It is important to seek help from professionals such as physical therapists to receive professional assistance and recommendations.
Activity modification: limit exposure to symptom provoking activity.
The primary goal of initial injury management is to manage symptoms. This may include avoidance of rapid movements, heavy lifting or dynamic/uncontrolled situations.
If you are an athlete, other options may include reducing overall workload or intensity of exercise, and limiting range of motion.
Oftentimes, athlete may become fear avoidant of performing a movement similar to the one that caused the injury. This, other goals may include improving confidence with movement. This can be achieved by the above mentioned recommendations.
If you would like to speak to Physiotherapists or to book an appointment please call 786-475-3094 or email: info@drabbate.com